Search Results Integrations
Overview
The <search-results-page> web component allows seamless integration of AI-powered search results and conversational AI capabilities into your HTML pages. Unlike the modal dialog search control (<ai12z-cta>), this component displays as a full page element. This component is loaded from a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and can be customized through a variety of properties.
Setup
Insert the following script and stylesheet in the head section of your HTML:
<script
type="module"
src="https://cdn.ai12z.net/pkg/ai12z@latest/dist/esm/library.js"
></script>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.ai12z.net/pkg/ai12z@latest/dist/library/library.css"
/>
Add the Component
You can insert the <search-results-page> into your HTML. This tag supports customization via the dialog agent->controls->search-results-page
Example HTML page
<html>
<head>
<script
type="module"
src="https://cdn.ai12z.net/pkg/ai12z@latest/dist/esm/library.js"
></script>
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.ai12z.net/pkg/ai12z@latest/dist/library/library.css"
/>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<search-results-page data-key="your_api_key_here"></search-results-page>
</div>
</body>
</html>
data-key
Locate the data-key in agent->agent settings, It's the API key
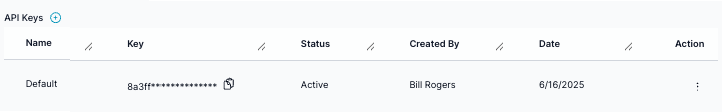
Add config-id, if you have more than one config for search-results-page, under agent->controls->search-results-page. You can have more than one config, if no config-id, it uses the default config
Control Attributes
The control contains following properties to customize the page.
| Property | Description | Example | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| data-key (Required) | API key from your ai12z Agent settings | data-key="123456" | |
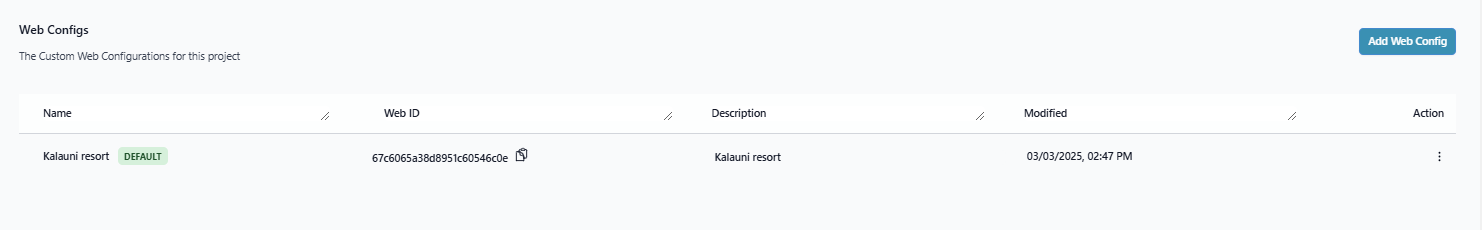
| config-id (Optional) | Load the settings based on config id. | config-id="1234567891" |
The below image will contains the config id.
Configure the data-key, data-mode and config-id via Javascript
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
const searchResult = document.querySelector("search-results-page")
searchResult.setAttribute("data-key", "XYZ")
searchResult.setAttribute("data-mode", "dev")
searchResult.setAttribute("config-id", "1234")
})
</script>
🔗 searchText URL Parameter
You can pre-fill the search input and trigger the component's behavior by including the searchText parameter in the URL. For example:
https://yourdomain.com/search?searchText=who%20is%20ai12z
Passing Objects
Options
This property allow us to pass the objects with key value pair to override the value which is set in the config page.
Example for passing the options
If it is a html page, we can customise like below
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
const searchElement = document.querySelector("search-results-page")
if (searchElement) {
//Add the language setting
searchElement.dataAttributes = {
lang: "hi",
}
//Add custom options as key value pair
searchElement.options = {
// Add your custom options here
}
}
})
</script>
Personalization of the bot
How to make the bot context-aware and tailor the experience by section.
Dynamic tokens (AnswerAI) or React System Prompts
Each system prompt supports dynamic tokens, so you can inject page-specific context and have the bot behave differently depending on where it's running: https://docs.ai12z.net/docs/ai-settings/answer-ai
Two especially useful tokens:
-
{attributes}Lets you insert additional information at runtime. You'd use JavaScript to pass whatever you want (e.g., page type, product category, logged-in state, language, etc.), and then reference it in your system prompt to guide behavior. -
{origin}Inserts the URL of the page the chatbot is on.
For the implementation details, see the "Passing attributes and tags" section below.
Recommendation: multiple welcome messages via Bot Configs
I also recommend creating two separate welcome messages (e.g., one for Support and one for the broader site experience) by using different Bot Configs:
Web Controls → <search-results-page> → "Add Bot Config"
Then embed the component like this:
<search-results-page
data-key="your_api_key_here"
config-id="your_config_id"
></search-results-page>
For example, your Support section can have a very specific support-oriented welcome message, while other sections can use a different tone and set of suggested actions.
How to debug
Within an agent, navigate to the agent settings, turn on debugging, then ask a question, navigate the Data view where you can see the question asked, if you open the metadata you can see what is being injected into the system prompt, for attributes or origin.
Passing attributes and tags
Attributes
Developer can pass a dictionary of additional data that can be used in prompts if you include the attribute tag in Answer AI.
IncludeTags
Array of tags, only content with one of these tags will be returned.
ExcludeTags
Array of tags, content will be excluded if it has one of these tags.
Example for passing the attributes, excludeTags and includeTags
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function () {
const ele = document.querySelector("search-results-page")
if (ele) {
ele.excludeTags = ["blog"]
ele.includeTags = []
ele.dataAttributes = {
content: {
newlist: [
{
_uid: "BUY6Drn9e1",
component: "foo",
headline: "Foo",
},
{
_uid: "gJZoSLkfZV",
component: "bar",
title: "Bar",
},
{
_uid: "X1JAfdsZxy",
component: "foo",
headline: "Another headline",
},
],
},
}
}
})
</script>
Events
The following events emitted by the component. You can subscribe to these events to execute custom logic in response to specific actions or state changes within the component.
1. errored
Description:
Emitted when an error occurs within the component. This event provides error details that can be used for logging or displaying error messages to the user.
Usage Example:
// Assuming 'searchComponent' is a reference to your component
searchComponent.addEventListener("errored", (event) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", event.detail)
})
Explanation:
- Listener: Attach an event listener to the
erroredevent. - Event Object: The callback function receives an
eventobject. - Error Details: Access the error information via
event.detail.
2. buttonClicked
Description:
Emitted when a button within the component is clicked. Useful for triggering actions in response to user interactions.
Usage Example:
searchComponent.addEventListener("buttonClicked", (event) => {
console.log("Button was clicked:", event.detail)
// You can access additional data from event.detail if provided
})
Explanation:
- User Interaction: Respond to button clicks inside the component.
- Custom Data:
event.detailcontains information about which button was clicked.
3. messageSent
Description:
Emitted when the component sends a message. This can be used to track outgoing messages or to update the UI accordingly.
Usage Example:
searchComponent.addEventListener("messageSent", (event) => {
console.log("Message sent:", event.detail)
// Update message list or notify other components
})
Explanation:
- Messaging Logic: Useful in chat applications or components that handle communication.
- Event Data:
event.detailcontains the message content or metadata.
4. messageReceived
Description:
Emitted when the component receives a message. Allows you to handle incoming messages and update the interface or state.
Usage Example:
searchComponent.addEventListener("messageReceived", (event) => {
console.log("Message received:", event.detail)
// Display the message or process it as needed
})
Explanation:
- Incoming Messages: Essential for handling data received from external sources or services.
- Processing Data: Utilize
event.detailto access message content.
Custom Methods
| Method Name | Description | How to use it |
|---|---|---|
| sendMessage | This method allows us to send a message programmatically. It accepts two parameters. Message (Required) – The first parameter must be a string containing the message to be sent to the server to be processed by the ai12z server the React LLM. Display Text (Optional) – The second parameter is optional and should be a string that specifies the display text for the message in the bot bubble. If the second parameter is not provided, the bot bubble will be use the first parameter | const searchElement = document.querySelector("search-results-page"); searchElement.sendMessage("What are the activities available","List all Activities") |
| sendJSON | This method allows us to send a JSON programmatically. It accepts two parameters. jsonData (Required) – The first parameter must be an object which will be sent to the server to be processed by a12z server React LLM. DisplayText(Required) – The second parameter should be a string that specifies the display text that the bot bubble will show. | const searchElement=document.querySelector("search-results-page");searchElement.sendJSON({"firstname":"xxxx","lastname":"yyyy","dob":"zzzz"}, "Info submitted"); |
General Usage Notes
- Event Subscription: Use the
addEventListenermethod to subscribe to events emitted by the component. - Event Object: The event listener callback receives an
eventobject, which may contain additional data inevent.detail. - Component Reference: Replace
searchComponentwith the actual reference to your component instance.
Example: Subscribing to Multiple Events
// Reference to your component
const searchComponent = document.querySelector("search-results-page")
// onErrored
searchComponent.addEventListener("errored", (event) => {
console.error("Error:", event.detail)
})
// onButtonClicked
searchComponent.addEventListener("buttonClicked", (event) => {
console.log("Button clicked:", event.detail)
})
// onMessageSent
searchComponent.addEventListener("messageSent", (event) => {
console.log("Sent message:", event.detail)
})
// onMessageReceived
searchComponent.addEventListener("messageReceived", (event) => {
console.log("Received message:", event.detail)
})
Tips for Handling Events
- Error Handling: Always check if
event.detailexists to avoid undefined errors. - Asynchronous Operations: If you're performing asynchronous tasks within the event handlers, consider using
async/awaitor.then()for Promises. - Unsubscribing Events: If necessary, remove event listeners using
removeEventListenerto prevent memory leaks.
// Removing an event listener
const onMessageReceivedHandler = (event) => {
console.log("Message received:", event.detail)
}
searchComponent.addEventListener("messageReceived", onMessageReceivedHandler)
// Later in your code
searchComponent.removeEventListener("messageReceived", onMessageReceivedHandler)
Conclusion
By subscribing to these events, you can effectively interact with the component and respond to its internal actions. This enables a more dynamic and responsive user experience.