MCP (Model Context Protocol) Setup
1. Select MCP as the Data Source
In the Properties dialog, set the Data Source to Model Context Protocol (MCP).
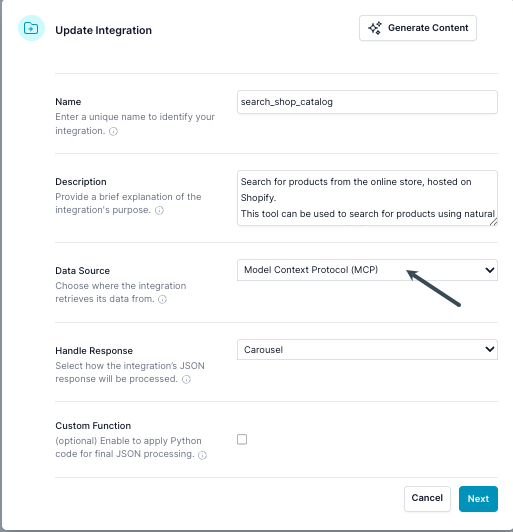
2. Configure MCP Server URL and Headers
In the Edit dialog, under the Model Context Protocol (MCP) section:
- Enter the MCP server endpoint URL.
- (Optional) Add any required HTTP headers, such as an API key or security token.
- (Optional) OAuth provider configuration
Tab API - MCP
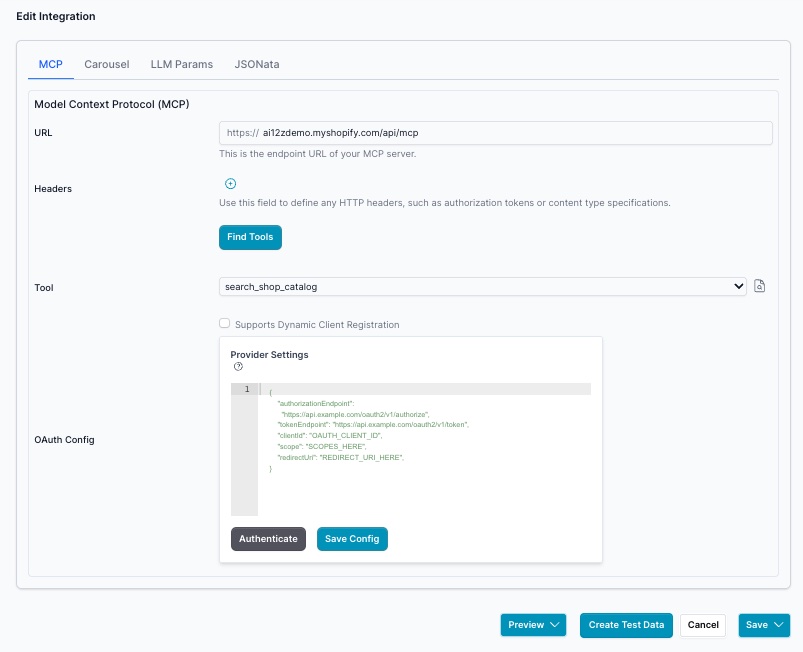
Tab Carousel
By default the Carousel should be "Custum". Vibe coding only works with custom
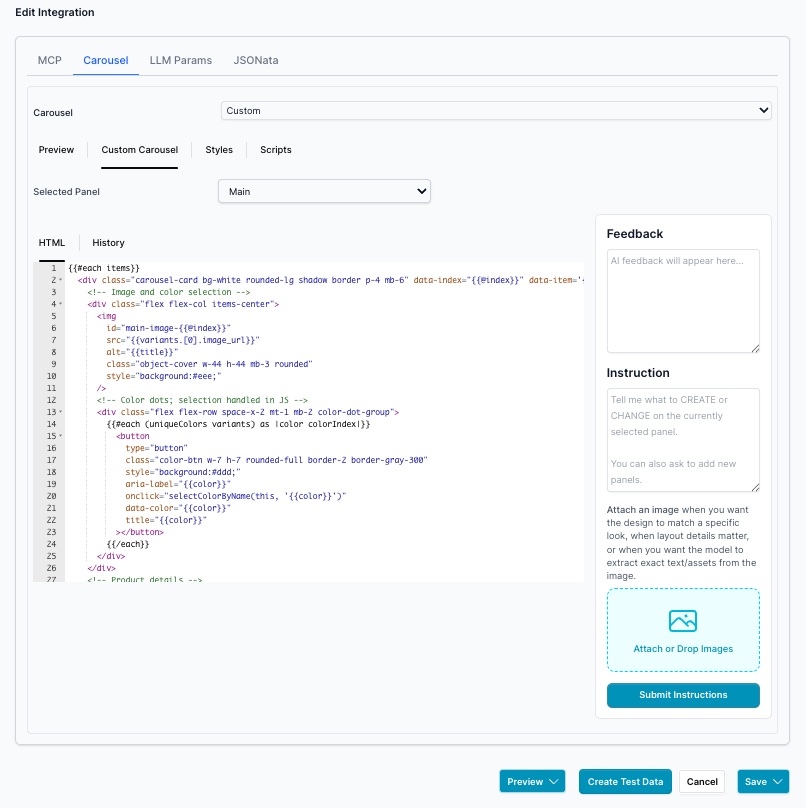
The Panels are selected by the Selected Panel, often only one
Vibe coding experience with update the Custom Carousel handlebars code, Styles and Scripts. Do vibe coding after you have collected test data.
Tab LLM Params
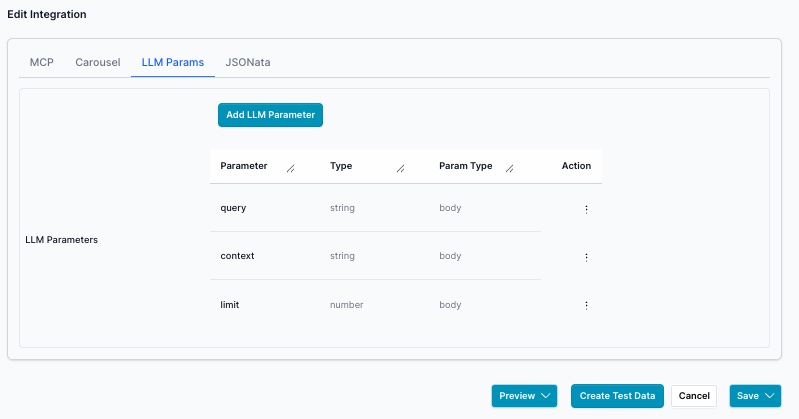
JSONata
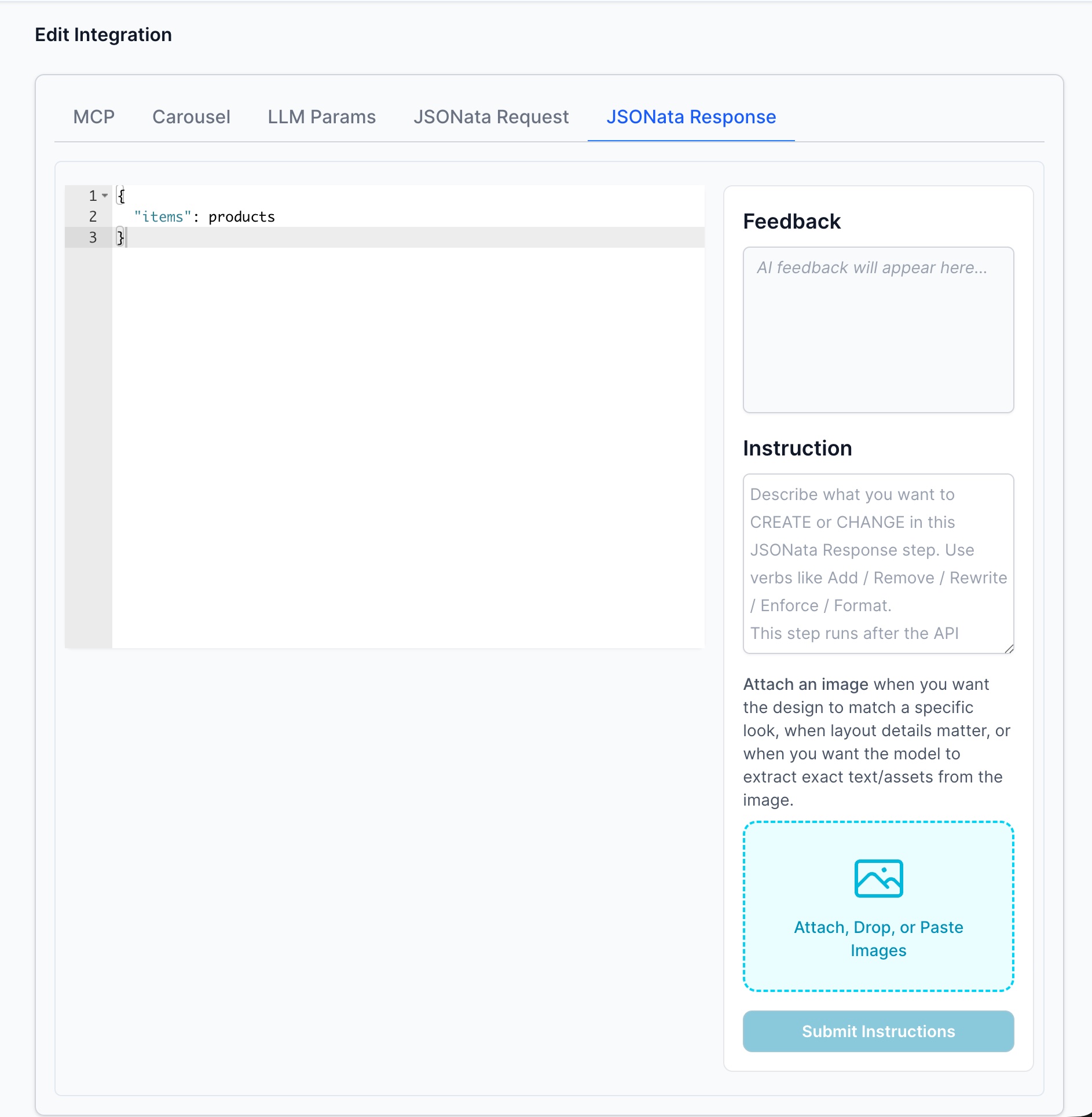
Note you need to return items array. If you endpoint does not return an array of items in this case an array of products you use JSONata to transform to items. It will not work if the array is not items and you plan to display a list.
3. Discover Tools
Click Find Tools to fetch the available tools from your MCP server.
- Select a tool from the dropdown.
- Click the magnifying glass icon to inspect the tool’s schema.
4. Review Tool Schema
Check the tool schema for required parameters. At minimum, you must provide all parameters marked as required.

5. Create Test Data
- Click the Create Test Data button.
- Fill in the property values (e.g.,
query,context,limit). - Click Send.
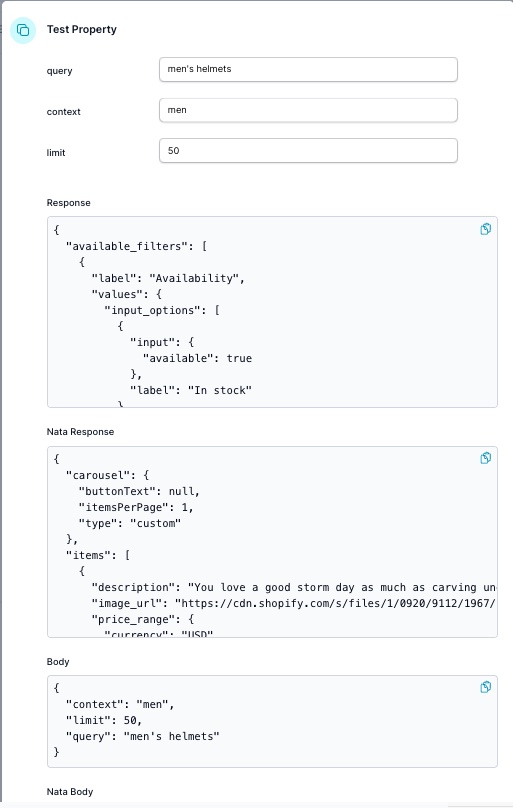
Review the Response section. If the array key is not items, you’ll need to map it in the next step.
Test button
View the results from the endpoint
Using Vibe coding
Vibe coding needs test data, so run this once, and its results are stored in the database. Note you need to use JSONata to transform to items as an array
You can upload a mock up of what you want to use for look and feel