Context AI & Building a Vector Query
Overview
Context AI is a LLM tool designed to enhance the capabilities of Language Model systems by constructing a more contextual vector query. This enhances the relevance of retrieved documents, making it more likely that the outcomes align closely with the user's needs. This AI is used only if it is the first query of the session then it uses the History AI.
Note: Check the AI settings --> ReAct & LLM Agent Settings --> Enable ReAct agentic workflow = Unchecked When Enable ReAct agentic workflow = Checked, then the React Reasoning Engine creates the vector query passed to the vector database
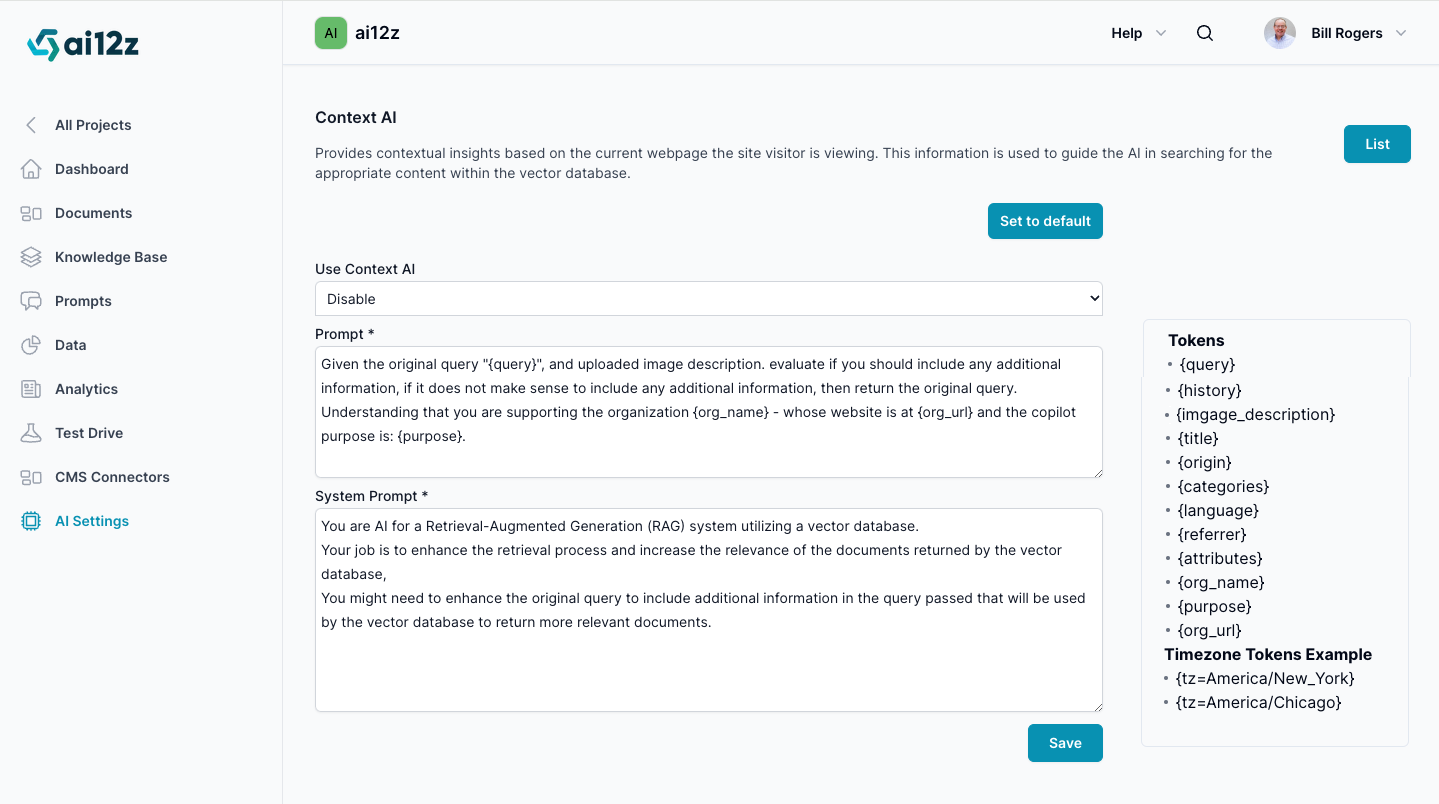
Selector, Use Context AI
Options are Disable, Auto and Enable. Auto means if Vision AI runs do not run. Not required for most co-pilots
Implementing Context AI
The process involves configuring two main components:
- The Prompt: The prompt for the Context LLM.
- The System Prompt: The System Prompt for the Context LLM.
By combining these with a list of dynamic tokens, Context AI customizes the query to fit the context of the organization using it, the purpose of the search, and the specifics of the user's request.
Configuring the Prompt
When setting up the prompt, it is essential to ensure that it accurately captures the user's intent and provides sufficient flexibility to adapt to different queries. Below is a template for configuring the prompt in Context AI:
Given the original query "{query}", evaluate if you should include any additional information. If it does not make sense to include any additional information, then just return the original query.
Understanding that you are supporting the organization {org_name} - whose website is at {org_url} and the copilot for {org_name} purpose is {purpose}.
Dynamic Tokens
Dynamic tokens act as placeholders that inject dynamic content into the prompt when it is executed. Context AI supports a range of tokens that you can utilize:
{query}: The user's inputted question.{image_description}The description from Vision AI{history}: The history of the conversation, allowing the AI to build upon previous interactions.{title}: The title of the webpage where the search is conducted, which may provide context for the search.{origin}: The original URL of the page, which might influence the type of information sought.{language}: The language of the page, ensuring that results are returned in the correct language.{referrer}: The URL that directed the user to the current page, which could influence their search intent.{attributes}: Additional context that can be inserted, typically added via javascript to the search control.{org_name}: The name of the organization for which the AI is configured, helping tailor the AI's function to that entity.{purpose}: The stated purpose of the AI bot, guiding the AI in how to prioritize and refine search results.{org_url}: The domain URL of the organization, which the bot can use to prioritize content from that domain.{tz=America/New_York}: Timezone creates the text of what is the time and date for the LLM to use{image_upload_description}: Image descriptions of images uploaded by the site visitor into the search box processed by vision AI
Best Practices
When writing prompts and configuring the system, here are some best practices to consider:
- Contextual Relevance: Always prioritize the user's intent and the context in which the query is made.
- Clear Token Usage: Use dynamic tokens precisely and only where they will enhance the quality of the query.
- Test and Iterate: Regularly test the prompts with real queries to ensure they perform as expected and iterate based on the results.
- Documentation: Maintain clear and comprehensive documentation so that the purpose and function of each token are easily understood by users configuring the AI.
Conclusion
By accurately configuring the prompt and system prompt, and utilizing the dynamic tokens, Context AI is capable of transforming a simple search into a complex, context-aware vector query. This results in a smarter search experience that saves time and delivers more relevant results.